Introduction
Here we will discuss about:
Sample function –
- Functions
- List Comprehensions
- Iterators and Generators
Functions
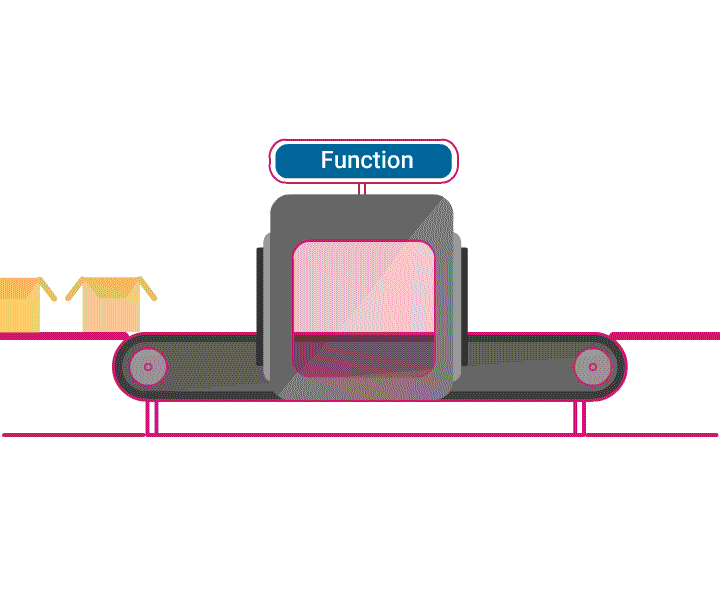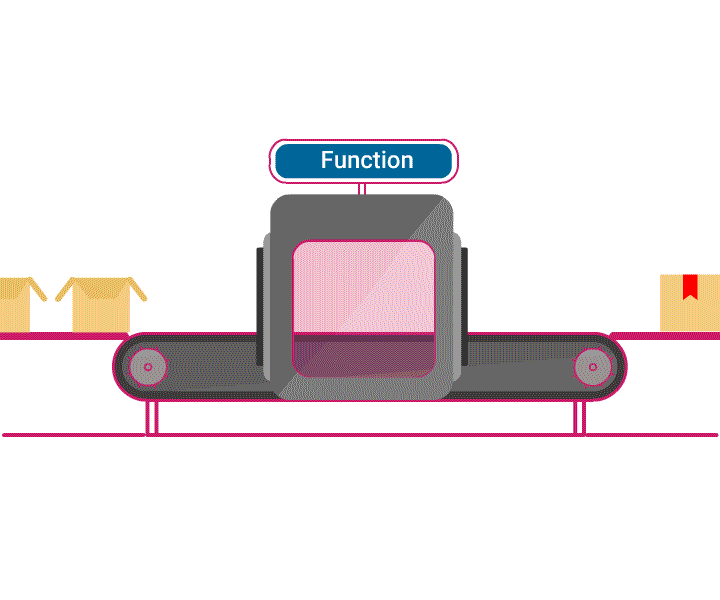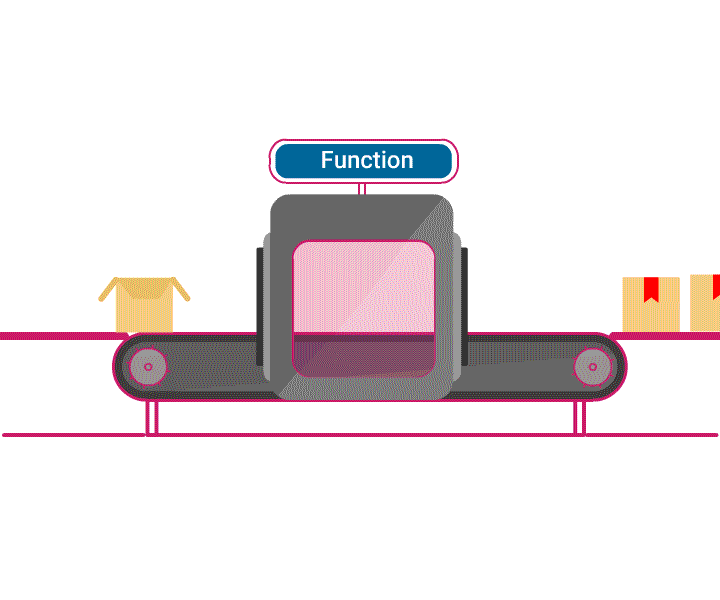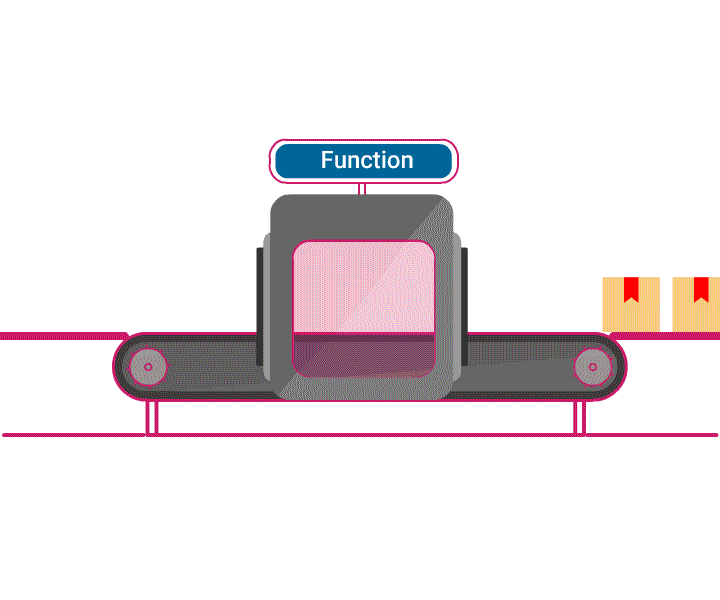
- A function is a piece of code, capable of performing a similar task repeatedly.
- It is defined using
defkeyword in python.
Syntax of a function :
def <function_name>(<parameter1>, <parameter2>, ...):
'Function documentation'
function_body
return <value>
- Parameters, return expression and documentation string are optional.
Sample function – square
def square(x):
'Returns square of a number.'
return x**2
Common Built-in Functions
There are many built-in functions Python offers. Here are some of them listed.
len: Returns the length of an object.- e.g :
len('hello') -> 5
- e.g :
type: Returns the type of an object.- e.g :
type([2,3]) -> <type list>
- e.g :
range: Returns a iterator of a number sequence.- e.g :
list(range(10, 13)) -> [10, 11, 12] list(range(3)) -> [0, 1, 2]
- e.g :
Iterators
- An Iterator is an object, which allows a programmer to traverse through all the elements of a collection, regardless of its specific implementation.
- Values of an Iterator can be accessed only once and in sequential order.
Sample Iterator
x = [6, 3, 1] s = iter(x) print(next(s)) # -> 6 print(next(s)) # -> 3 print(next(s)) # -> 1 print(next(s)) # -> StopIteration Error
List Comprehensions
- Alternative to for loops.
- More concise, readable, efficient and mimic functional programming style.
- Used to:
- Apply a method to all or specific elements of a list, and
- Filter elements of a list satisfying specific criteria.
Example
x = [6, 3, 1] y = [ i**2 for i in x ] # List Comprehension expression print(y) # -> [36, 9, 1]
Generators
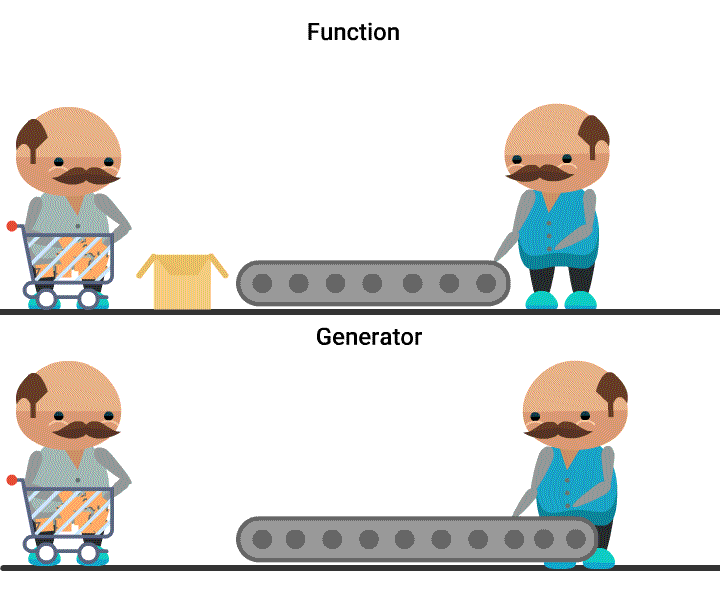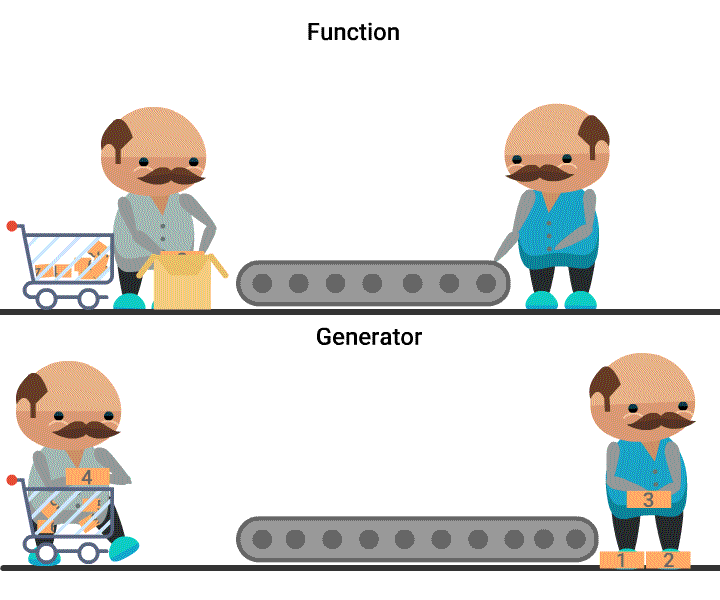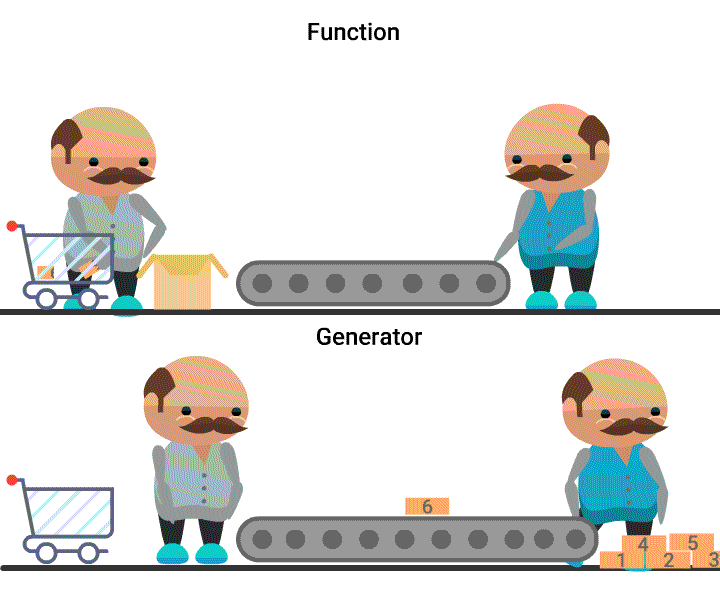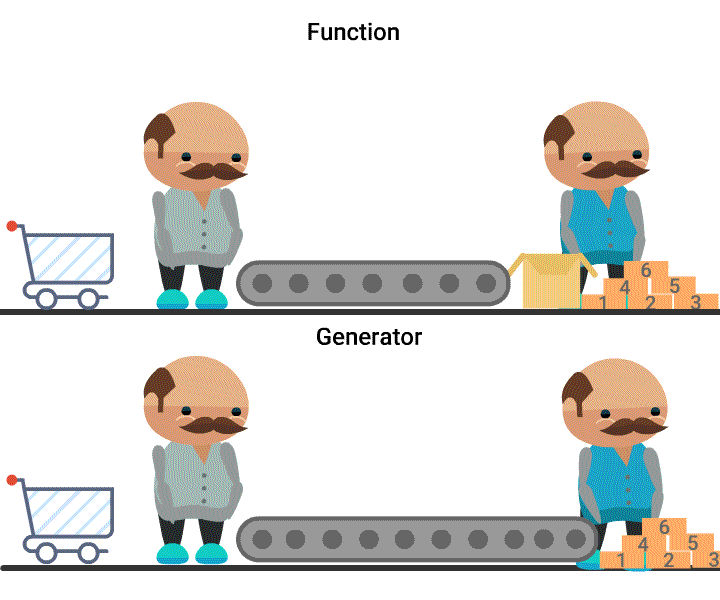
- A Generator object is an iterator, whose values are created at the time of accessing them.
- A generator can be obtained either from a generator expression or a generator function.
Example
x = [6, 3, 1] g = (i**2 for i in x) # generator expression print(next(g)) # -> 36